How To Use The Most Important Tools At Your Disposal
Campaign structure within Google Ads is notoriously undervalued. Developing the correct campaign structure will create a healthy foundation for your campaigns to prosper over a 2-4 year period.
Without the right campaign structure, your campaigns will deliver inconsistent numbers of leads and leads of inconsistent quality, resulting in frustration, confusion, and ultimately a drop in enrollments.

It is important to note that there isn’t a universal campaign structure that works for every company in every scenario. But, by aligning your goals or programs with your structure, you can develop a strategy that works best for your company.
We’ll start with the campaign/ad group structure for SEM.
SEM (Search Engine Marketing)
Below, we have outlined a few different campaign structure strategies depending on the type of data that is available and the number of program offerings.
Campaign Structure Example #1
Alpha – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – Exact
Alpha – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – BMM
Alpha – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – Phrase
Alpha – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – Broad
Beta – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – Exact
Beta – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – BMM
Beta – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – Phrase
Beta – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – Broad
Alpha
It refers only to queries that turned into a lead/application /enrollment (depending on which data is integrated into your Google Ads account).
Beta
If you have applications or enrollments data in your Google Ads platform, Beta queries are those that drive leads but not applications/enrollments for the purpose of testing. If you only have leads in your Google Ads platform, then Beta would represent the queries that are relevant but yet to generate a lead.
Campaign Structure Example #2
Local – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – Exact
Local – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – BMM
Local – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – Phrase
Local – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – Broad
National – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – Exact
National – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – BMM
National – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – Phrase
National – [Program Name] – Non-Branded – Broad
This campaign structure is primarily geared toward companies that have both online and on-campus programs with the focus on enrolling students from within a 100-200 mile radius while also driving online enrollments from outside the local region. The separation of “local” and “national” helps prioritize budgets broken out by these two segments.
Campaign Structure Example #3
This pertains to companies that offer programs in one primary field with overlapping subjects and keyword themes (e.g., medical online education).
Category 1 – Non-Branded – Exact
Category 2 – Non-Branded – Exact
Category 3 – Non-Branded – Exact
(Campaigns are duplicated to BMM, Phrase, and Broad)
Example Categories: general, competitors, specific themes.
Segmentation Explanations
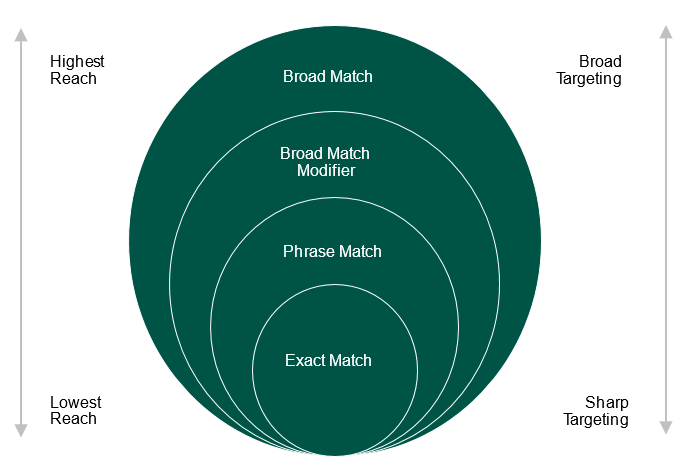
The most important segmentation element today is breaking down your campaigns by match types. Here is why.
Match type data vary dramatically when it comes to performance and quality of leads, so it’s crucial to keep them separated at a campaign level. In the data example below, you’ll see that Exact has the most leads, cheapest CPL, and highest conversion rate—and highest lead quality because it’s Exact.
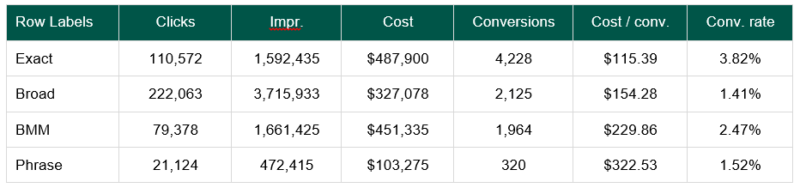
Broad has the second highest number of leads, but the lowest conversion rate. This means the quality of the leads is not as high when compared to Exact, BMM, and Phrase. BMM and Phrase are more on the expensive side but are also considered good quality because the words within the keyword exist in the query. The goal is to drive as many Exact leads as possible while using the other three match types to find new ways that people are searching for your program.
If you have a high number of poor quality leads, there is a high chance that the majority (80%+) of your budget is being spent on Broad match. Broad match can be highly effective if you have the proper campaign/negative keyword strategy in place (reference negative keyword section).
If you allow Broad match to be your primary match type, then your performance is going to vary tremendously on a daily basis and you will receive a significant amount of poor quality leads.
When your campaigns are broken down by match types, you gain the ability to do something called “bid tiering by match type.” This allows you to tier your bidding from highest to lowest (Exact to Broad).
The purpose of this bidding strategy is to force as much traffic to the Exact, Phrase, and BMM match type, leaving Broad match as a completely exploratory match type that fishes for new search queries. Below is an example of how to effectively tier bidding for each match type.
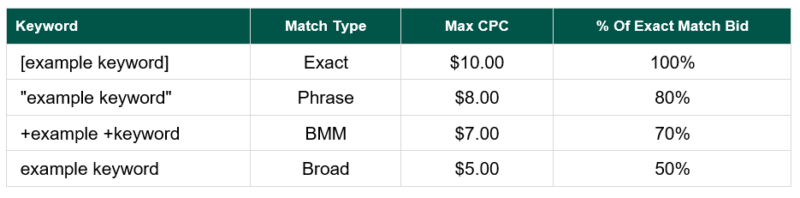
Hot tip: Be careful optimizing your Broad match campaigns. These campaigns have great potential for success, but you must make sure to not overpay for clicks by aggressively increasing your broad match CPCs.
Breaking down campaigns by match types also enables a strategy called “Cross-Match Negative Keywords.” This allows you to take all of your Exact match keywords and add them as a negative to the respective BMM, Phrase, and Broad campaigns. The goal is to ensure that your Exact match keywords get all the Exact match traffic while forcing the BMM, Phrase, and Broad campaigns to become the fishing match types driving new traffic and growing the account.
Additionally, you should have a few different negative keyword lists.
Master Negatives
The bread and butter of negative keywords. Master Negatives eliminate irrelevant queries from showing up in an account. This must be done on a regular basis in order to keep the account clean, as new irrelevant search queries will never stop showing up. Google has previously confirmed that 25% of all daily search queries are being seen for the first time. If you’re using broad match, there will always be negatives to add to an account.
Weekly is the recommended frequency, but bi-weekly or monthly is acceptable once most high-frequency irrelevant queries have been added to your negative keyword list.
There should also be a distinction between the Exact match negatives and your Phrase match for easier damage control. When adding Phrase match negatives, be careful of what you add, as you could unknowingly end up excluding a lot of traffic.
Bad Quality Leads
These are queries that are driving leads but are not driving applications or enrollments. We want to block all of these queries from all Phrase and BMM match campaigns to ensure we are continuously striving to improve quality.
Poor lead quality is a controversial topic in the education space. It hass prevented many education marketers from reaching their goals and caused many admissions teams to waste precious time and money on unqualified leads, which ultimately decreases the time spent on higher quality leads.

Another reason you might be experiencing a high number of poor quality leads is incorrect keyword selection. In order to determine which keywords make sense for your company, someone who is knowledgeable about your programs needs to review them. This also ensures that whatever keyword is being selected has the intent—or nearly has the intent—of following through to register for the program.
If a Broad keyword is driving only irrelevant queries, it should be paused and analyzed for quality. If it is driving both relevant and irrelevant queries, the negative strategy outlined above will help improve the keyword’s performance over time.
If you have access to lead quality data on the query level, you can look for trends and add an additional level of negatives. For example, a private education company with higher tuition will likely see worse performance than “cheap college degree” or “low cost design program” searches, even if both searches are driving leads.
Final Tips On Negatives
- Don’t apply negative lists to exact match campaigns.
- Separate Exact vs. Phrase match master negatives for easier management and damage control.
- When doing cross-match negatives, do not include keywords that are too long and can, therefore, be considered “low search volume” by Google. 40+ characters is a good guideline.
- Cross-match negatives are only updated at the launch of the campaigns and when new keywords are added to the campaigns.
- Master/bad quality negative lists should be updated on a weekly basis.
Ad Group Structure
Your ad groups should be tightly themed categories. This allows you to look at the ad group naming convention and immediately understand which keywords are in that ad group without having to see the actual keywords. 
Once the ad groups are tightly themed—usually 3-6 keywords per ad group—you can create Ads that are directly based on the exact keywords that people are using to search for your company. For Broad, you can get more creative with your headlines because Broad keywords match with a wider range of queries. Aim for the highest possible CTR!
YouTube/Display Campaign Structure And Settings
An effective YouTube strategy requires a multi-layered approach, taking into account the various options for engaging with your target audience. A popular way to break out your campaigns is by separating them by the types of audiences you are targeting.
For example, in order to increase specificity, you might build out campaigns structured around the following types of audiences:
- Affinity
- In-Market
- Custom intent
- Remarketing
Though all of these audiences can be a valuable component of your video or display campaign strategy, you will most likely find some of them to be far more effective than others in driving action throughout your lead funnel. Building out your campaigns in this way allows you to allocate budget accordingly and focus your spend on the most successful audiences.
Certain conditions, however, might warrant breaking down and structuring campaigns with more granularity. These conditions include geographical targeting, language, or categories of programs.
If you offer many types of programs, you can break down your targeting by program. This can keep your budgets aligned with specific program goals and prevent a more popular program from going through the entire budget. You will also be able to use different program-specific ad creative based on the audience type.
Ad Groups
Inside your YouTube campaigns, each one of your ad groups should be centered around a specific audience that coincides with the broader theme of the campaign. For example, your custom intent campaign might include ad groups focused on various types of custom intent audiences built around different keyword lists. Additionally, ad groups can be broken out even further based on factors like age, gender, and other demographic details.
Structuring your ad groups in this manner creates the opportunity to show the most relevant ad creative for the given audience. This greatly increases the likelihood of further engagement with your content.
Other Key Video Campaign Settings
Much like any campaign on Google, success can easily be derailed if your campaign settings are incorrect. A few quick notes about some settings you’ll want to pay special attention to:
- Location targeting
Careful consideration should be given to the locations you want your ads to target. Depending on your video advertising budget, you may wish to limit campaign geographical targeting to a more confined area than your search efforts. We always recommend excluding regions where you don’t want to pay for traffic. If you have a physical campus, you can limit some campaigns to local prospective students who are more likely to enroll and allow those campaigns to run at higher CPA targets. - Networks
By default, most video ads are eligible to be shown on video partner sites in Google’s Display Network. While you may or may not want to exclude these placements from consideration for your video ads, we do recommend keeping a close eye on the traffic they bring in. We often find that this traffic is of poorer quality than general YouTube traffic. Thus, many of our clients have simply opted to turn it off. - Bidding strategy
If you are running a campaign that is focused on driving conversions, you may find that there are limited options for bidding strategies. In most conversion-focused campaigns, you will have the option to run either a “maximize conversions” strategy or a “target CPA” strategy. Both of these approaches require accurate conversion tracking. You must also select the conversions you wish to optimize toward in the campaign “conversions” setting.
The “maximize conversions” strategy allows Google Ads to set bids automatically to help you get the most conversions within your budget. Starting with this strategy gives the Google algorithm more flexibility to test your traffic and determine which ad placements and audiences are most likely to convert.
Once you have some data under your belt, you can consider switching to Target CPA, which will give the Google algorithm a specific cost-per-conversion to aim for.
If you import leads as well as applications into Google, you can run a lead generation campaign with the goal of generating leads for a low cost, and a performance campaign with the goal of maximizing applications.
The lead gen campaign will likely end up driving more traffic, which will be very useful for remarketing. However, traffic from the performance campaign will likely be of higher quality.
Content Exclusions
As important as it is to identify ad placements you wish to serve, it can be equally—if not more—important to identify placements you don't want to serve. Google gives you several exclusion options you can utilize to reduce poor-quality traffic.
These options are:
- Inventory type limitations
You can choose between Expanded, Standard and Limited inventories, which range from least to most restrictive based on profanity, sexual content and violence within content.

- Excluded content
You can specifically opt out of content that fits into certain categories. These categories are tragedy and conflict, sensitive social issues, sexually suggestive content, sensational and shocking, and profanity and rough language. This exclusion setting gives you more control than the "inventory type" setting. - Excluded types and labels
It prevents your ad from showing on video content that belongs to any of the categories below:- Placement exclusions
You can get really granular and exclude specific websites, channels, videos, apps, or app categories from showing your ads. - Excluded topics
You may also select from a wide range of YouTube video topic categories on which you don’t want your ads to display.
- Placement exclusions
Increase Enrollments For Your Organization
Is increasing enrollment important to you and your organization? Are you looking for ways to increase digital engagement? If yes, make sure to read How eLearning Organizations Can Drive Profitable Enrollments At Scale With Google Ads In 2020 and harness the amazing power of Google Ads to help enrollment grow.

